Climate Action
Climate Action
Location-based solutions drive successful adaptation and mitigation

Climate Action
Location-based solutions drive successful adaptation and mitigation

Geography is key to climate resilience
Today, organizations are finding new ways to adapt and thrive with geospatial technology that is uniquely poised to meet this moment.
The life-altering effects of a changing climate are inherently geographic. Risks, impacts, and solutions exist in specific places and require location-based problem-solving.
A geographic approach
Understanding climate data in the context of location helps decision-makers model scenarios, pinpoint risk, and adapt.
Location technology
Geographic information system (GIS) technology provides the tools to collect, view, manage, analyze, and share climate data.

Insights that fuel action
Business, government, and community leaders use location intelligence from GIS analysis to understand changing conditions and act quickly.
A proven leader in climate risk analytics
Organizations around the world use Esri’s geospatial technology to promote sustainable solutions to the climate crisis.
Facilitating progress
Hundreds of thousands of organizations globally, including Fortune 500 companies, rely on Esri’s GIS technology to inform strategic decisions.
Building the world’s most powerful GIS
Esri’s GIS software provides trusted mapping and spatial analytics plus access to thousands of authoritative datasets, maps, and expert guidance.

A recognized leader
The Forrester New Wave™: Climate Risk Analytics, Q4 2022 report recognizes Esri for its leading data visualizations and advanced data processing.

If you have physical assets that could be threatened by climate, Esri can bring the data and processes to bear to target operational resiliency opportunities.
–The Forrester New Wave™: Climate Risk Analytics, Q4 2022
Understand climate risk with the powerful
analytics and high-tech maps in GIS
Dynamic maps enriched with accurate data reveal patterns, trends, and relationships that help leaders
address risks from climate-related events.
Flooding
Drought
Wildfire
Extreme heat
Extreme heat
Flooding
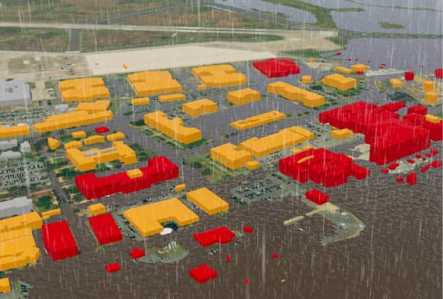
Modeling flooding impacts with projections tailored to specific infrastructure and assets provides the precision decision-makers need to prepare for any scenario—from the best-case scenario to the worst.
Modeling potential sea level rise in 2100 first shows impacted areas and then where a sea wall (light blue) would protect buildings.
Drought
With spatial analysis and visualizations of drought-impacted areas, leaders can make informed decisions to ensure water resources can sustain energy, agriculture, and residential needs in the future.
As drought conditions threaten agricultural areas along the Po River in Italy, suitability analysis shows the ideal locations for reservoirs that can supplement water resources.
Wildfire
Maps of historic and real-time wildfire data and predictive analytics inform climate-aware plans that safeguard communities, critical infrastructure, and forest ecosystems.
A map showing electric transmission lines and areas of increasing wildfire risk reveals where to prioritize clearing vegetation to reduce risk.
Extreme heat
Spatial analytics provide an intuitive way to understand the multi-dimensional nature of extreme heat with maps that reveal areas of high vulnerability. Leaders can use those insights to better manage changing needs and determine ideal places for efforts such as green space development.
In this neighborhood in Rio de Janeiro, visualizing urban heat, existing tree canopy, and population density on a single map reveals where planting trees will lower temperatures for the most people.
Biodiversity loss
Accessing and mapping robust data on species, protected areas, and human activity reveal the places where focused climate action can safeguard the long- term health of the planet.

As lynx on the Iberian Peninsula need to migrate north toward more suitable habitat, spatial analysis shows where wildlife corridors would support the most efficient path.
Take climate action with GIS
GIS connects data and analysis to provide a holistic picture of current and future climate-related
hazards. These insights inform new climate action solutions that will protect people and places.
Mapping and visualization
Dynamic maps provide an intuitive way to investigate, understand, and share complex climate data. Rich visualizations reveal the best places for proactive measures.
Mapping and visualization
Comprehensive, intuitive analytical tools help people throughout organizations extract deep insights from vast amounts of data.
Predictive modeling
3D modeling and geospatial artificial intelligence help organizations forecast future scenarios, anticipate problems, and understand potential decision outcomes.
Authoritative data
Access to ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World, the most comprehensive collection of global geographic information, and other trusted data sources gives organizations of all sizes the information they need to make data-driven decisions.
How organizations are solving climate challenges
Framework for climate resilience
Esri’s GIS technology provides a powerful framework for visualizing and understanding massive
amounts of climate data. The Climate Checklist details how government and business leaders can
use this this proven approach to assess and minimize climate risks using GIS technology.
Understand and explore hazards
Visualize all relevant climate risk data in one place to determine potential impacts on people, assets, and networks.
Analyze and assess vulnerabilities
Examine all relevant data—including operational, demographic, and streaming data—to reveal relationships and understand risk now and in the future.
Investigate and communicate
Engage stakeholders with interactive maps that create a shared understanding of climate risks and mitigation strategies.
Prioritize and plan
Use 3D models to simulate a variety of climate-related situations and assess possible outcomes on networks and communities.
Take action
Use location-based insights and climate action hubs to inform strategic plans, coordinate efforts, and monitor progress.
Geography is key to climate resilience
Today, organizations are finding new ways to adapt and thrive with geospatial technology that is uniquely poised to meet this moment.
The life-altering effects of a changing climate are inherently geographic. Risks, impacts, and solutions exist in specific places and require location-based problem-solving.
A geographic approach
Understanding climate data in the context of location helps decision-makers model scenarios, pinpoint risk, and adapt.

Location technology
Geographic information system (GIS) technology provides the tools to collect, view, manage, analyze, and share climate data.

Insights that fuel action
Business, government, and community leaders use location intelligence from GIS analysis to understand changing conditions and act quickly.
A proven leader in climate risk analytics
Organizations around the world use Esri’s geospatial technology to promote sustainable solutions to the climate crisis.
Facilitating progress
Hundreds of thousands of organizations globally, including Fortune 500 companies, rely on Esri’s GIS technology to inform strategic decisions.
Building the world’s most powerful GIS
Esri’s GIS software provides trusted mapping and spatial analytics plus access to thousands of authoritative datasets, maps, and expert guidance.

A recognized leader
The Forrester New Wave™: Climate Risk Analytics, Q4 2022 report recognizes Esri for its leading data visualizations and advanced data processing.
If you have physical assets that could be threatened by climate, Esri can bring the data and processes to bear to target operational resiliency opportunities.
–The Forrester New Wave™: Climate Risk Analytics, Q4 2022
Understand climate risk with the powerful
analytics and high-tech maps in GIS
Dynamic maps enriched with accurate data reveal patterns, trends, and relationships that help leaders address risks from climate-related events.
Flooding
Drought
Wildfire
Extreme heat
Biodiversity loss
Flooding
Modeling flooding impacts with projections tailored to specific infrastructure and assets provides the precision decision-makers need to prepare for any scenario—from the best-case scenario to the worst.
Modeling potential sea level rise in 2100 first shows impacted areas and then where a sea wall (light blue) would protect buildings.
Drought
With spatial analysis and visualizations of drought-impacted areas, leaders can make informed decisions to ensure water resources can sustain energy, agriculture, and residential needs in the future.
As drought conditions threaten agricultural areas along the Po River in Italy, suitability analysis shows the ideal locations for reservoirs that can supplement water resources.
Wildfire
Maps of historic and real-time wildfire data and predictive analytics inform climate-aware plans that safeguard communities, critical infrastructure, and forest ecosystems.
A map showing electric transmission lines and areas of increasing wildfire risk reveals where to prioritize clearing vegetation to reduce risk.
Extreme heat
Spatial analytics provide an intuitive way to understand the multi-dimensional nature of extreme heat with maps that reveal areas of high vulnerability. Leaders can use those insights to better manage changing needs and determine ideal places for efforts such as green space development.
In this neighborhood in Rio de Janeiro, visualizing urban heat, existing tree canopy, and population density on a single map reveals where planting trees will lower temperatures for the most people.
Biodiversity loss
Accessing and mapping robust data on species, protected areas, and human activity reveal the places where focused climate action can safeguard the long- term health of the planet.
As lynx on the Iberian Peninsula need to migrate north toward more suitable habitat, spatial analysis shows where wildlife corridors would support the most efficient path.
Take climate action with GIS
GIS connects data and analysis to provide a holistic picture of current and future climate-related hazards. These insights inform new climate action solutions that will protect people and places.
Mapping and visualization
Dynamic maps provide an intuitive way to investigate, understand, and share complex climate data. Rich visualizations reveal the best places for proactive measures.
Mapping and visualization
Comprehensive, intuitive analytical tools help people throughout organizations extract deep insights from vast amounts of data.
Predictive modeling
3D modeling and geospatial artificial intelligence help organizations forecast future scenarios, anticipate problems, and understand potential decision outcomes.
Authoritative data
Access to ArcGIS Living Atlas of the World, the most comprehensive collection of global geographic information, and other trusted data sources gives organizations of all sizes the information they need to make data-driven decisions.
How organizations are solving climate challenges
Framework for climate resilience
Esri’s GIS technology provides a powerful framework for visualizing and understanding massive amounts of climate data. The Climate Checklist details how government and business leaders can use this this proven approach to assess and minimize climate risks using GIS technology.
Understand and explore hazards
Visualize all relevant climate risk data in one place to determine potential impacts on people, assets, and networks.
Analyze and assess vulnerabilities
Examine all relevant data—including operational, demographic, and streaming data—to reveal relationships and understand risk now and in the future.
Investigate and communicate
Engage stakeholders with interactive maps that create a shared understanding of climate risks and mitigation strategies.
Prioritize and plan
Use 3D models to simulate a variety of climate-related situations and assess possible outcomes on networks and communities.
Take action
Use location-based insights and climate action hubs to inform strategic plans, coordinate efforts, and monitor progress.