Geography and Government
A geographic approach informs policy, operations, and planning for improved decision-making across communities.
Geography and Government
A geographic approach informs policy, operations, and planning for improved decision-making across communities.
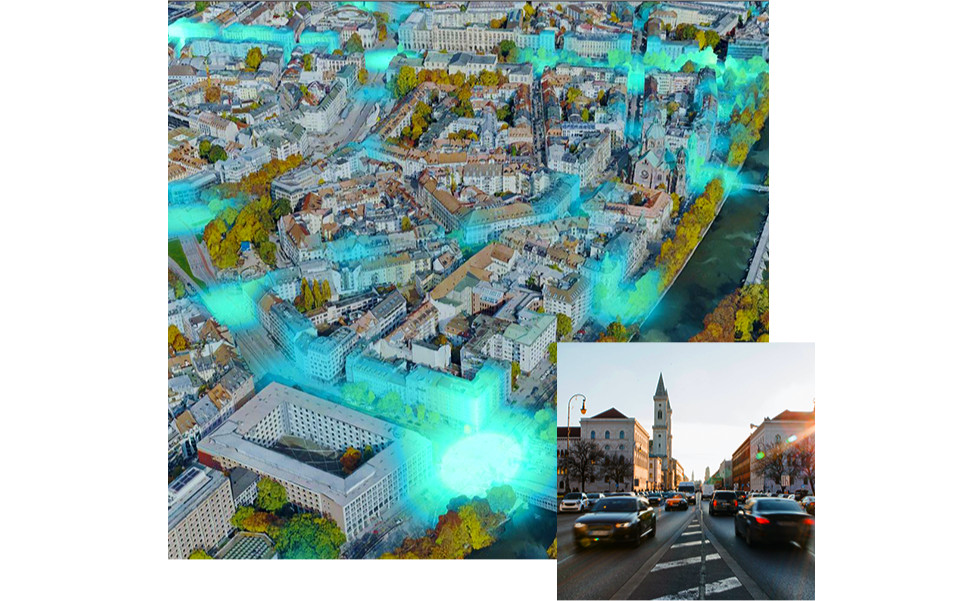

How do governments benefit from a geographic approach?
Government leaders take a geographic approach to shape priorities, policies, and engagement. Leveraging geographic information system (GIS) technology, they use maps, apps, analytics, and dashboards to manage issues such as equity, economic development, transit, land management, health, and safety.
Build intelligent, resilient infrastructure
Key to upgrading critical assets is understanding how infrastructure relates to communities and natural systems—what is happening where. Infrastructure systems are being infused with technologies including GIS, digital twins, sensors, and advanced analytics.
Asset and network management: Monitor asset location, condition, performance, and life cycle.
Planning and logistics: Share information to prevent disruption.
Operational awareness and efficiency: Watch workflows in real time.
Prioritization and equity: Reveal patterns of inequality.
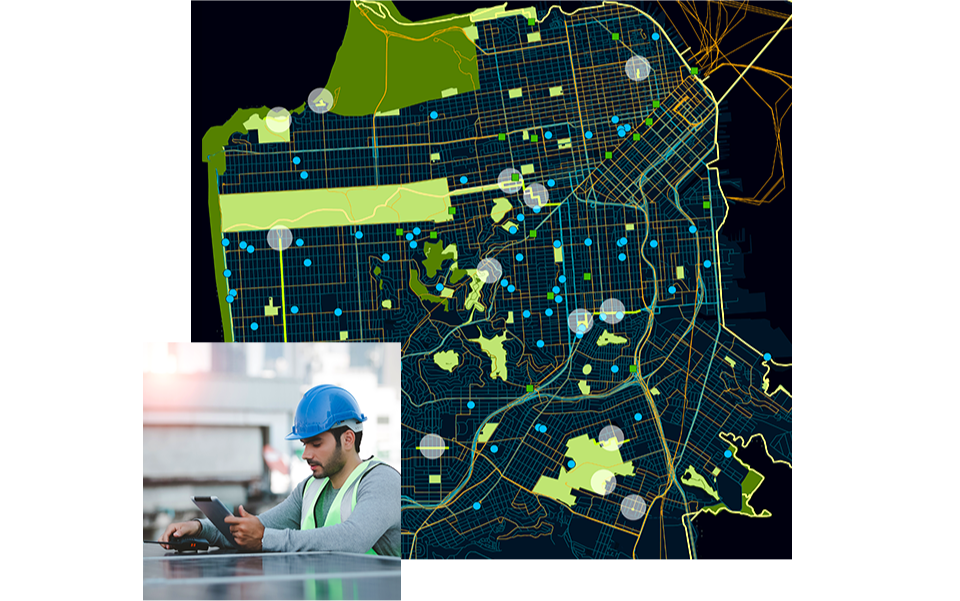

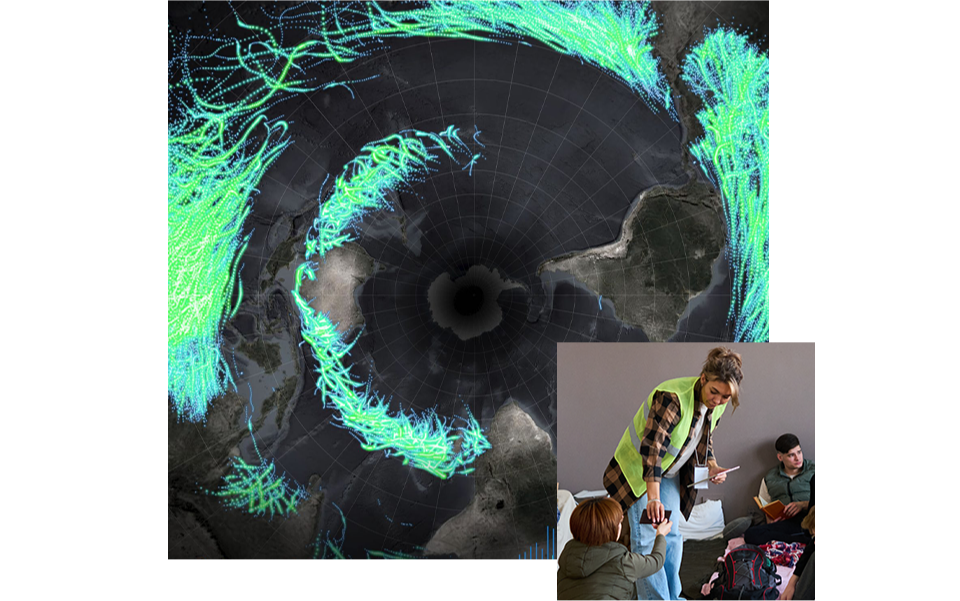
Respond to disasters and prepare for climate change
Geography is a powerful tool in response and risk mitigation, empowering government leaders to anticipate weather events and climate impacts and plan accordingly.
Monitor situations in real time.
Track incidents and resources.
Know the status of vulnerable people and assets.
Model scenarios to aid prevention and response.
Spatial analysis informs data-driven planning
A geographic approach to government supports agility. Leaders of smart cities and counties use
GIS to prioritize infrastructure investments and optimize planning and policy decisions, such as
where to create sustainable housing or green space.
Maps inform planning and recovery
Geospatial analysis highlights risks to create a base of knowledge for improving safety and
mitigating threats. Officials use a geographic approach to government to enhance
collaboration across departments and support recovery efforts.
How do governments benefit from a geographic approach?
Government leaders take a geographic approach to shape priorities, policies, and engagement. Leveraging geographic information system (GIS) technology, they use maps, apps, analytics, and dashboards to manage issues such as equity, economic development, transit, land management, health, and safety.

Build intelligent, resilient infrastructure
Key to upgrading critical assets is understanding how infrastructure relates to communities and natural systems—what is happening where. Infrastructure systems are being infused with technologies including GIS, digital twins, sensors, and advanced analytics.
Asset and network management: Monitor asset location, condition, performance, and life cycle.
Planning and logistics: Share information to prevent disruption.
Operational awareness and efficiency: Watch workflows in real time.
Prioritization and equity: Reveal patterns of inequality.

Respond to disasters and prepare for climate change
Geography is a powerful tool in response and risk mitigation, empowering government leaders to anticipate weather events and climate impacts and plan accordingly.
Monitor situations in real time.
Track incidents and resources.
Know the status of vulnerable people and assets.
Model scenarios to aid prevention and response.

Spatial analysis informs data-driven planning
A geographic approach to government supports agility. Leaders of smart cities and counties use GIS to prioritize infrastructure investments and optimize planning and policy decisions, such as where to create sustainable housing or green space.
Maps inform planning and recovery
Geospatial analysis highlights risks to create a base of knowledge for improving safety and mitigating threats. Officials use a geographic approach to government to enhance collaboration across departments and support recovery efforts.
