Geometric Networks
Best Utility Network Data Model Available in ArcMap
Geometric Networks with ArcMap offer a way to model common networks and infrastructures found in the real world. Water distribution, electrical lines, gas pipelines, telephone services, and water flow in a stream are all examples of resource flows that can be modeled and analyzed using a geometric network.
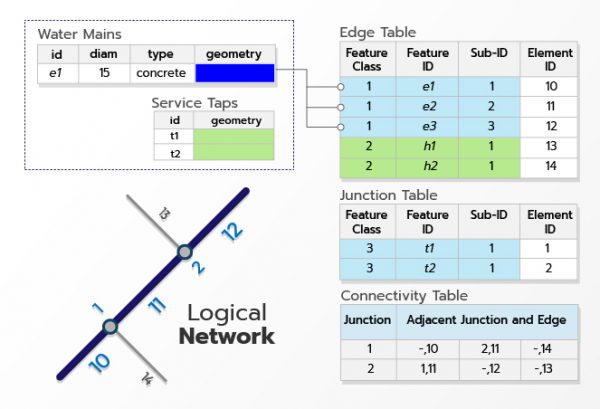
A geometric networks is a set of connected edges and junctions, along with connectivity rules, that are used to represent and model the behavior of a common network infrastructure in the real world. Geodatabase feature classes are used as the data sources to define the geometric network. You define the roles that various features will play in the geometric network and rules for how resources flow through the geometric network.
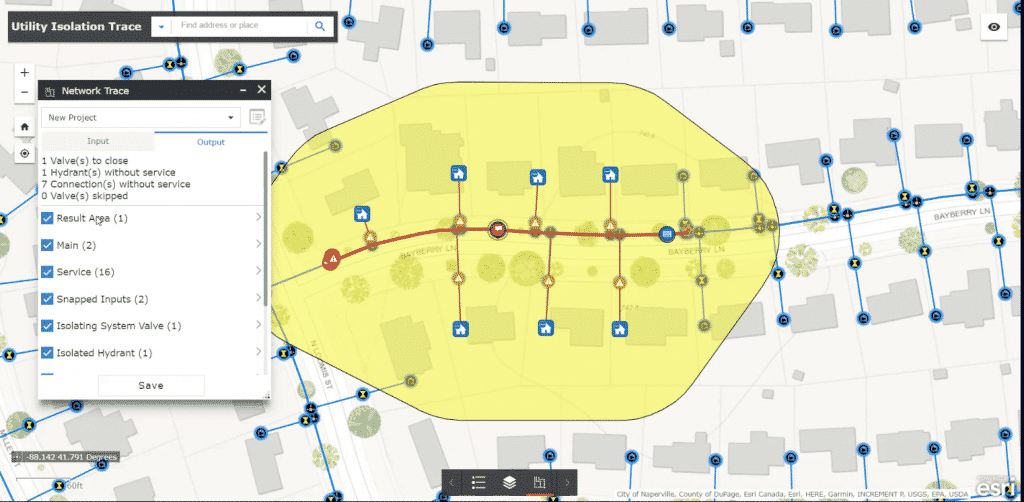
Once a geometric network is modeled, you can benefit from performing various network analyses. The following table lists some of the analyses that can be performed and provides an example of who might benefit from each kind of analysis.
Geometric Networks with ArcMap offer a way to model common networks and infrastructures found in the real world. Water distribution, electrical lines, gas pipelines, telephone services, and water flow in a stream are all examples of resource flows that can be modeled and analyzed using a geometric network.
A geometric networks is a set of connected edges and junctions, along with connectivity rules, that are used to represent and model the behavior of a common network infrastructure in the real world. Geodatabase feature classes are used as the data sources to define the geometric network. You define the roles that various features will play in the geometric network and rules for how resources flow through the geometric network.

Once a geometric network is modeled, you can benefit from performing various network analyses. The following table lists some of the analyses that can be performed and provides an example of who might benefit from each kind of analysis.
